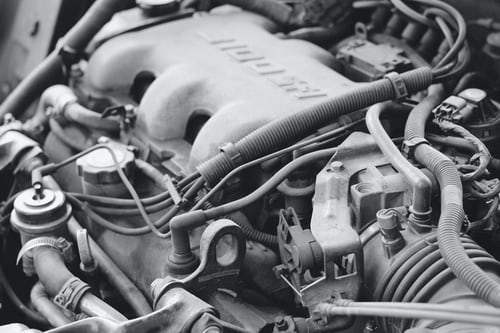
The standard combustion engine used in today's automobiles, trucks, and SUVs is known to have over 250 individual parts. But did you know that gaskets, which are mounted between two other pieces, are among the most vital parts? Despite their small size and lack of complexity, they are critical to engine operation.
Several types of gaskets are used in different engine parts. Some gaskets are located inside the device, while others attach the engine to helping components such as the air intake, exhaust pipe, and water pumps. Their primary function is to keep contaminants out of the engine, maintain constant internal pressure, and maintain oil and other fluids within the engine. Here are the most significant gaskets on your engine and why they are so essential to its operation.
Cylinder Head Gaskets
The cylinder head gasket, also defined as the head gasket, stops combustion gases from entering the coolant pump. They're usually made of copper and sit between both the engine block and cylinder head. The compression ratio within the combustor can be affected by the size of the gasket.
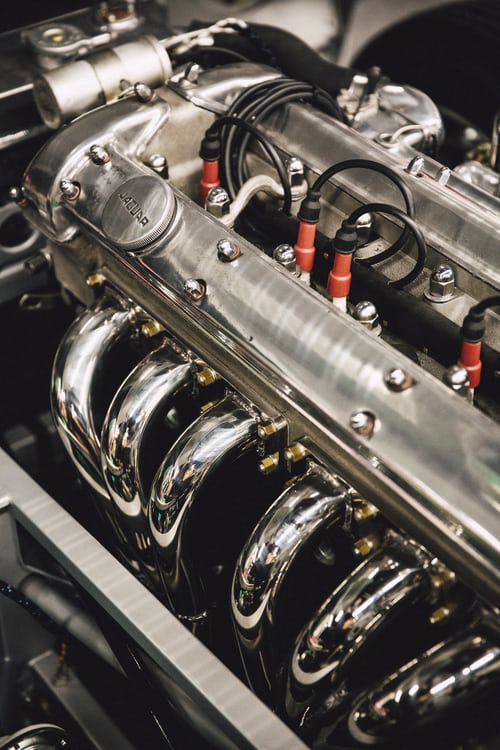

Head gaskets on old cars had a "shelf life" and it would wear out, particularly near the sides of the combustion chamber due to increased heat. This would reduce the load inside the combustion chamber, potentially resulting in equipment failure.
Despite the fact that today's head gaskets are far better designed, one issue they always have will be getting damaged during overheating circumstances. Coolant seeps into the combustor and mixes with fuel oil when a head gasket fails. This can result in substantial engine damage, necessitating a full engine repair or replacement.
Don’t wait till then if you have to replace your engine gaskets Australia has loads of places you can get it done from. Your nearest mechanic can help you.
Exhaust and Intake Manifolds Gaskets
The intake manifold gasket controls temperature of the chamber and prevents air from leaking during combustion. This ensures that the fuel mixture contains the proper concentration of oxygen for the engine to run efficiently.
The exhaust manifold is identical, but it sits between the exhaust manifold and cylinder head. Whenever these gaskets fail, it can cause compression problems and reduce engine performance. When a car is maintained properly with scheduled maintenance, these gaskets seldom malfunction.
Main Bearing Gaskets
The main bearing gasket's aim is to hold the oils in the oil pan while the crankshaft rotates. It is situated at the back of the engine, just off the last main bearing. To withstand extreme temps, the seal or gasket is usually made of silicone or rubber. It prevents oil from flowing past the crankshaft as it turns. The main bearing sealing will fail if there is too much oil pressure, too much heat, or too much engine sludge, which is prompted by not adjusting the engine oil and filter as prescribed.

Camshaft Gaskets
A gasket is also needed for the camshaft to stop oil from spilling out. The round rubber gasket, also known as a cam seal, serves two functions. It not only stops oil from leaking, but it also prevents dirt and dust from entering the piston and causing harm.
If a defective gasket is not replaced, it may cause significant damage over time. While certain external gaskets can be changed by a licensed mobile mechanic, internal engine gaskets should be repaired by a specialized engine shop. It is important to have a technician check the engine gaskets to determine when they need to be replaced.